Giant volumes of secret data are available to India’s insurance companies. One violation may reveal policyholder identities, financial data, and perhaps even health records, with crores of damages and administrative punishment. Given this danger, IRDAI Certification places concrete security testing results above mere policy papers. The IRDAI cybersecurity standards for 2026 demand proof not only on paper but also in reality that your systems are safe if your company manages policies, claims, premium payments, or digital consumer journeys.
This book examines the right positioning of VAPT from insurance companies inside the IRDAI framework. You will learn why most teams fail, how VAPT helps the IRDAI data protection plan, and what auditors really search for during an IRDAI cybersecurity audit. From a last-minute checklist rush to a consistent, repeatable compliance system is the aim.
Many insurance companies collaborate with specialized testing firms instead of creating everything in-house to streamline execution.
Why Is IRDAI Certification Important?
To add organization and responsibility to security among insurers, brokers, and digital insurance platforms, the IRDAI unveiled its Information and Cyber Security Guidelines. The IRDAI Information and Cyber Security Guidelines, 2023, which broaden the existing 2017 framework and include all prominent actors in the insurance value chain, have updated these.
IRDAI certification effectively confirms your company’s end-to-end security profile. From KYC and onboarding to claims and policy servicing, you should safeguard consumer data throughout its life cycle. You must show that your top-level authorized and documented security protocols are always in place. This includes incident response, change management, access control, and risk management.
Furthermore, the certificate affirms your routine VAPT for insurance companies, continuous monitoring of systems processing policyholder data, and annual IRDAI cybersecurity audits. It demonstrates that you satisfy the IRDAI framework for data protection, which calls for access control, encryption, retention discipline, and breach management. One of the most obvious signs for clients, partners, and reinsurers that an insurance company treats cyber risk seriously now is IRDAI certification.
What are the New IRDAI Cybersecurity Guidelines 2026?
Building on the 2023 information and cybersecurity standards, the IRDAI cybersecurity guidelines 2026 encourage insurance firms toward more evidence-backed and operationally-based security. They are now dissatisfied with vague assertions that such systems are secure. Instead, they call for proven evidence of particular treatments taken and assessed. This aligns perfectly with the amended IRDAI Information and Cyber Security Guidelines, 2023, which demand board monitoring, clearly established roles, and technical safeguards throughout data, applications, and infrastructure.
Insurance first needs complete data visibility. That entails charting how policyholder data interacts with which third parties or cloud services, where it is stored, how it is entered into applications, and where it is processed. Observations or more extensive scoping during an IRDAI cybersecurity audit often result from missing or obsolete diagrams. Second, the rules promote evidence-based cybersecurity. Auditors want pictures of remediation, log extract samples, configuration exports, and VAPT reports demonstrating how problems were discovered, ranked, and resolved.
Third, there is a greater anticipation for ongoing risk monitoring. This trend follows CERT In’s Comprehensive Cyber Security Audit Policy Guidelines, which stress constant threat preparation above one-time audit operations. Regular vulnerability scans are anticipated from insurers as well as cloud posture monitoring, and prompt CERT in advisory response. At last, vendor responsibility has tightened. Including TPAs, web aggregators, or SaaS suppliers, any partner who deals with policyholder data has to satisfy similar security criteria and submit VAPT or audit reports when asked.
Why Is Vapt Non-negotiable For IRDAI Certification?
Due to the kind of data insurers have, Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing (VAPT) is at the core of the IRDAI security model. Together, rich targets for attackers are policy papers, bank statements, contact information, medical records, and claims histories. IRDAI does not wish to depend just on firewall diagrams and policies. It seeks evidence that trained specialists tried to break your systems and that you corrected their discovered flaws.
VAPT reports help demonstrate, during an IRDAI cybersecurity audit, that your consumer sites, mobile apps, APIs, internal tools, or network perimeter do not have any readily exploitable flaws. They demonstrate the least privileged access in your cloud setups and whether internal networks are appropriately segmented. They also show how authorized roles only have access to sensitive data that is encrypted both at rest and in transit.
Furthermore, supporting the regulator’s expectation of a complete risk remediation lifecycle are VAPT reports. Good reports will list problems by severity, link them to CVSS ratings, and include retest data demonstrating the correction of high-risk and serious vulnerabilities. CERT, in particular, encourages this severity-based approach and the use of standard scoring systems, which fit well with IRDAI’s emphasis on structured risk management, in recent guidelines on cybersecurity audits.
Which IRDAI-mandated Security Controls Must Vapt Validate?
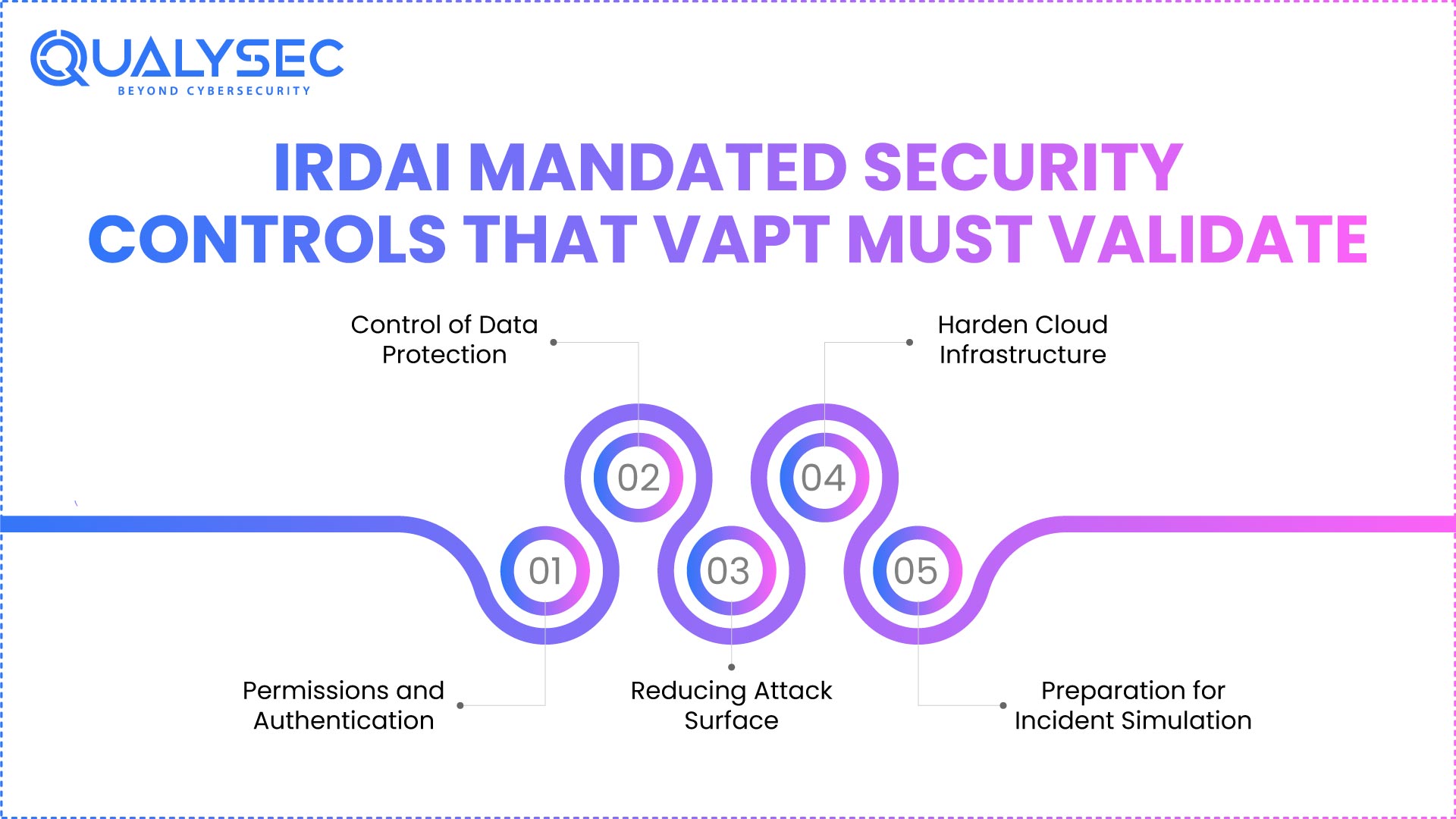
IRDAI cares more about which security measures were confirmed than whether you name a test “application VAPT” or “network VAPT.” Under an IRDAI framework, VAPT has to demonstrate that particular required control points are operating properly and are not bypassable in reality.
1. Permissions and Authentication
VAPT needs to check that strong authentication is applied for important systems like admin portals, internal consoles, and dashboards. Generally, this implies rigorous password or credential policies for all users as well as multi-factor authentication for privileged accounts. Testers attempt to circumvent login procedures, use weak passwords, or reuse stolen credentials.
2. Control of Data Protection
According to the IRDAI data protection framework, sensitive data must be encrypted at rest and in transit; personally identifiable information cannot be left open or preserved as plaintext. VAPT helps in this by looking at how apps and APIs manage data and by searching for intelligible text transfers over HTTP or misconfigured TLS.
3. Reducing Attack Surface
IRDAI expects controlled businesses to keep a limited, properly managed external attack surface. Consequently, VAPT involves finding exposed services, forgotten subdomains, unsecured test cases, and unneeded open ports. Any exposed admin panel or debug interface is regarded as a major omission.
4. Harden Cloud Infrastructure
As additional insurers switch to AWS, Azure, or GCP, cloud setup has become a regular cause of nonadherence. VAPT and configuration checks verify that IAM roles follow least privilege, that storage buckets are not publicly exposed, and that security groups and firewall rules do not inadvertently open internal services to the internet. Read more on Cloud Infrastructure security
5. Preparation for Incident Simulation
At last, IRDAI and CERT are both going toward a threat readiness approach rather than only checklist compliance. By simulating real attacks and seeing if your monitoring systems notice them, VAPT assists you. The aim is to determine whether warnings are produced, logs record the events, and your team may look into and react.
IRDAI Security Controls Vs. Vapt Validation Demands
The table below offers a summary of how core IRDAI control expectations match with VAPT validation. When you go over the scope with your security partner, this can serve as a high-level IRDAI compliance checklist.
| IRDAI Control Requirement | What VAPT Must Validate |
| Authentication security | MFA usage, privilege enforcement, and absence of weak default credentials |
| Data protection | Correct IAM roles, secure buckets, and isolated VPC design |
| Application integrity | Firewall hygiene, limited open ports, and proper segmentation |
| Network access control | No injection, tampering,g or business logic flaws |
| Cloud governance | Logging, alerting, and response capabilities for attack attempts |
| Incident readiness | Correct IAM roles, secure buckets, and an isolated VPC design |
You should correlate every IRDAI control to at least one test scenario when planning testing. Your reports will speak the same language as the guidelines; hence, your auditor won’t have to guess which test covers which control.
What Should A Practical IRDAI Compliance Checklist Include?
Usually, four categories make up a practical IRDAI compliance checklist for security teams. Using this architecture guarantees that VAPT, governance, and reporting all advance together rather than alone.
1. Documentation
From board-level monitoring to operational duties, you want an updated Information Security Policy that references the most recent IRDAI cybersecurity criteria 2026 and distinctly allocates responsibilities. Data flow diagrams should illustrate how information of policyholders traverses systems, including cloud services and third-party interfaces. Applications, infrastructure, APIs, and external services processing regulated data have to be included in a unified asset inventory.
2. Technical Restrictions
Technically, the checklist covers IAM, segmentation, patching, and encryption. IAM has to abolish inactive or orphaned accounts and demand least privilege and multi-factor authentication for administrators. Network segmentation should guarantee that internet-facing systems have to go through regulated zones before they may directly access databases or core policy systems.
3. Validation and Testing
Under validation and testing, the checklist should specify annual VAPT for insurance companies, encompassing all essential applications, networks, and cloud assets. With proof linked to the original report, high and critical findings have to be corrected within predetermined timelines and then retested. Cloud security audits ought to check configuration standards and find drift over time.
4. Official Reporting
On the reporting side, IRDAI wants logs to be kept for at least 180 days and to be available for forensic investigation. On demand, your IRDAI cybersecurity audit reports, VAPT summaries, and repair records must be accessible for review. You must also follow deadlines for informing IRDAI of any major data leaks or cyber attacks.
How Does an IRDAI Cybersecurity Audit Actually Proceed Step By Step?
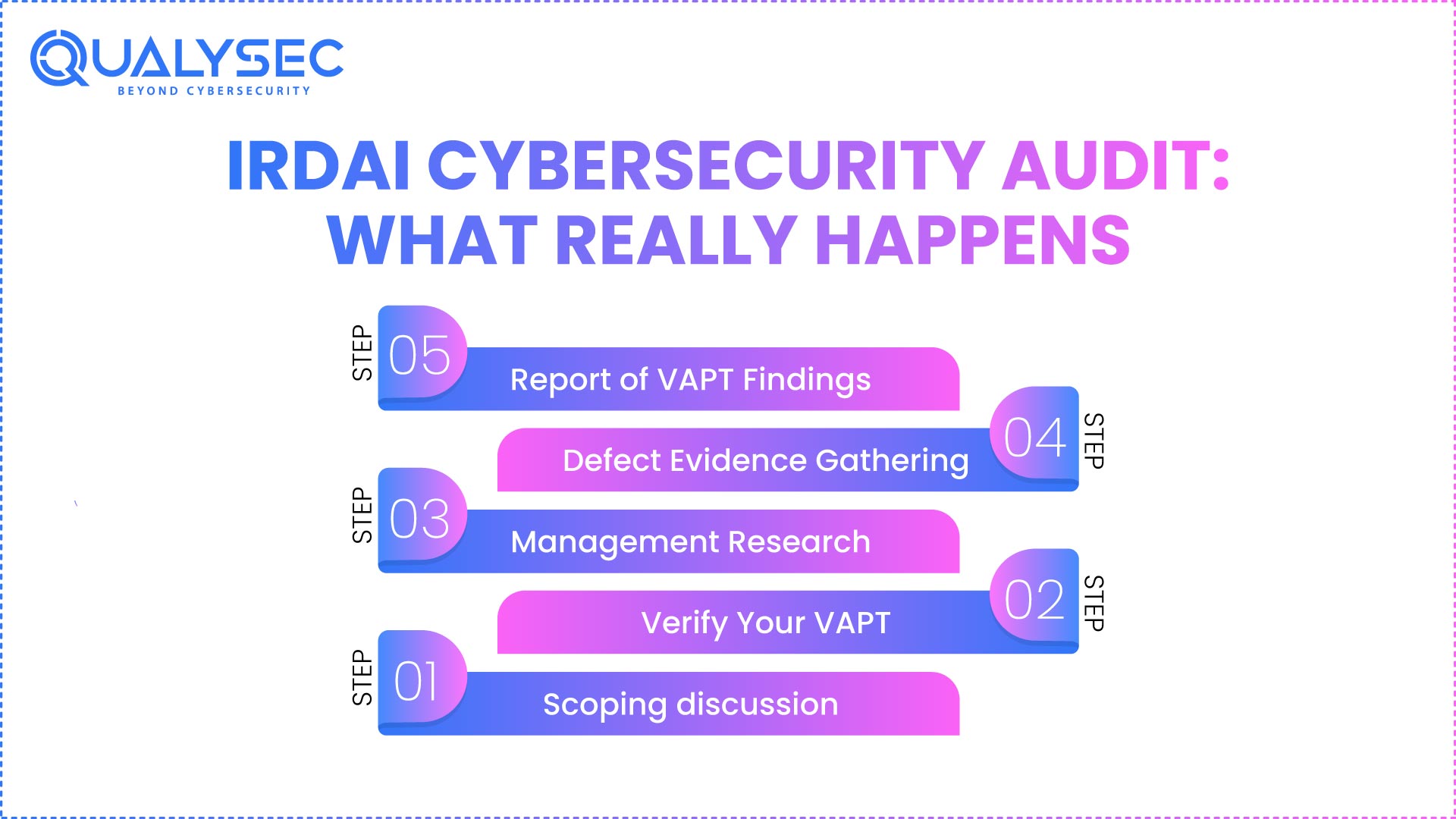
Usually following a predictable order, an IRDAI cybersecurity assessment will differ in particulars between the auditor and the company. Understanding this flow enables you to anticipate the correct artifacts and save from final-minute firefighting.
Step 1: Scoping discussion
Auditors first assist you in defining the scope. They identify back-office systems, databases, cloud components, and key client-facing programs. They also consider collaborations with external entities, including aggregators, payment gateways, and TPAs. Auditors may either expand your scope or note this as a risk if your asset inventory is low or your scope seems incomplete.
You need to prepare yourself mentally, assess the situation, and produce a detailed data flow diagram to reduce the shocks at this stage. Prior work on your IRDAI compliance checklist pays off now. It helps you appreciate how things are interconnected and which systems control the details of the policyholders.
Step 2: Verify Your VAPT
Auditors analyze your VAPT information next. They assess the retests, the methods employed, and the ratings given to the issues concerning their severity and scope. The value of reports is higher when you adhere to particular patterns and remain compliant with IRDAI. If auditors encounter significant or ambiguous issues, they may require you to rectify these issues promptly and perform retests afterwards.
Partnering with a firm like Qualysec, which produces reports in compliance with CERT-In and IRDAI, could ease this stage. Their VAPT reports provide auditors a way to assess their risk level without much trouble, as they supply detailed severity mapping and tracking of resolutions.
Recommended read: Get your free VAPT audit guide from Qualysec
Stage 3: Management Research
At this point, the auditors examine the IAM logs, check the methods of access, look at the schedule of patches, and review the configurations of the plundering cloud. Some auditors may request verification of access control, approval samples, or evidence of periodic updates. Effectively designed monitoring systems facilitate the auditors’ ability to confirm whether the important systems are being monitored and whether the systems are being logged on.
Particularly with IAM, storage access, and security group rules, cloud environments are given careful consideration. Auditors may consult earlier circulars of IRDAI’s 2023 recommendations and framework for cybersecurity, as needed to understand the control requirements.
Step 4: Defect Evidence Gathering
When there are discrepancies or findings to be confirmed by auditors, they collect evidence such as log exports, configuration snippets, policies, and screenshots. In some instances, they are required to demonstrate ascertained and unambiguous specific controls and unambiguous VAPT results.
Establishing a centralized repository or keeping a sealed evidence binder that organizes significant effort. To elaborate on a simple IRDAI audit pack, internal teams or Qualysec update it every year. This is what most insurers rely on with VAPT reports and risk logs, as well as VAPT primary policies.
Step 5: Report of VAPT Findings
Once the defects are reviewed and enough evidence is disclosed, the auditor compiles a report confirming perpetual compliance or the sufficiency of evidence provided in support of your IRDAI certification. In the case where there are still major deficiencies, they might take the position of providing a conditional approval, where there would be further compliance verification and testing or amendments as corrections.
Prudent attention to your VAPT process and paperwork may prove helpful in minimizing the risk of undesirable complications during the final phase.
If you want to align your next audit cycle with best practices, you can start by scheduling an assessment with Qualysec!
Speak directly with Qualysec’s certified professionals to identify vulnerabilities before attackers do.
Why Do Companies Commonly Fail IRDAI Compliance Checks?
Vulnerabilities, such as easily guessable passwords, are what a great number of articles tend to focus on. However, in the case of insurance companies, they do not deal with some of the other structural issues that have a direct impact on their compliance during the IRDAI inspection.
1. Multiple Policies of the Cloud Provider
While checking the cloud provider’s IAM policies, you see that the roles assigned to the resources are granting permission too liberally. They may be allowing full access to the storage and compute services, which is certainly not ideal. With roles that are at risk, the auditors expect a strict role-based access policy to be in effect, and less permissive access is geared toward the role.
2. Assets that are shadowed
Unaccounted-for proof-of-concept systems, unregistered test servers, and legacy systems are examples of assets that continue to exist while processing real data. Such assets can lead an auditor to question the boundary of your defined asset management scope, and in the case they’re found, the auditor may expand the view of your assets or arrive at a different conclusion.
3. Present logs without a link
Many companies gather logs but do not centrally administer or assess them. IRDAI projects real monitoring, not just warehousing. If you cannot prove your capacity to spot suspicious behavior, audits frequently raise issues on event readiness.
Typical Irdai Audit Errors And Methods To Prevent Them
From a compliance and VAPT perspective, the table below lists some typical causes of failure together with the associated preventive measures.
| Failure Cause | Prevention Strategy |
| Shadow IT assets | Use automated discovery tools and maintain a central asset list |
| Weak cloud IAM | Redesign roles with least privilege and regular permission review |
| Missing remediation proof | Capture screenshots, tickets and retest reports for every fix |
| Enforce annual vendor VAPT and contract-level security clauses | Capture screenshots, tickets, and retest reports for every fix |
| Logs not correlated | Implement a SIEM or central log management and alerting process |
Considering this table, a little IRDAI compliance checklist during planning will enable you to prevent typical mistakes. Qualysec can also check your surroundings against these patterns and conduct focused testing to verify that high-risk areas like IAM, logging, and third-party integrations are under control.
What Benefits Does Vapt Deliver Beyond IRDAI Requirements?
While much of this handbook is about compliance, VAPT for insurance firms provides advantages beyond meeting the IRDAI cybersecurity requirements of 2026. A strong testing strategy ensures that digital journeys from policy purchase through claims tracking are secure and reliable, therefore raising consumer confidence. Typically, when people confidently use your apps and websites, adoption increases and support expenses decrease.
Regular VAPT also lowers the severity and likelihood of cyber incidents. Early detection of flaws enables you to avoid the reputational damage and regulatory reporting related to significant breaches. By highlighting legacy systems, delicate integrations, and costly workarounds, VAPT results enable technology leaders to plan modernization in a more informed way over time.
How Qualysec Can Help You Achieve IRDAI Certification
Organized, audit-ready security testing for India’s regulated sectors, which include insurance, is what Qualysec provides. They are aware of how the IRDAI data protection system, the IRDAI cybersecurity guidelines 2026, and the IRDAI certification convert into practical test scenarios and paperwork needs.
I. Complete VAPT for IRDAI Certification
From mobile apps and web applications to APIs, network perimeters, and cloud settings, Qualysec offers thorough VAPT. Their approach adheres to CERT, OWASP, and industrial norms. Though in aligned practices, it is always customized to your actual systems rather than using a fixed template, ranking results so your teams know which to handle first, with clear severity mapping, helps you to do so.
Their papers include technological details, proof of exploitation, and clear business impact arguments since their target audience is auditors.
II. Revisions and Corrective Measures
Qualysec helps your development and infrastructure teams beyond spotting problems with proof of concept materials, repair instructions, and retesting. They make sure that auditors find proof of the acceptable gathered repair and that large gaps are properly sealed.
Rechecking is seen as a legitimate stage of the relationship rather than as an afterthought. This satisfies IRDAI’s expectation that high-risk issues are validated as settled rather than just noted as corrected on an internal tracker.
III. IRDAI Evidence and Supporting Documents
According to IRDAI standards, Qualysec enables you to improve or develop your documents. Personal VAPT findings may be linked to IRDAI control standards and CERT In guidance, as well as risk registers, VAPT summary dashboards, and compliance mapping matrices, therefore encompassing evidence bundles.
They could also support someone in compiling a package for an audit that includes relevant policies, diagrams, logs, and testing results. This speeds up faster certification cycles and helps to lower disagreement across every IRDAI cybersecurity evaluation.
Conclusion
Originally a checkbox exercise, IRDAI certification has become a physical standard of cyber maturity for the Indian insurance sector. Along with the improved 2023 information and cybersecurity framework and the IRDAI cybersecurity criteria 2026, regulators now anticipate insurers to exhibit genuine resilience backed by VAPT reports, cloud hardening evidence, and clearly defined processes implementing the IRDAI data protection framework.
Viewing VAPT, documentation, monitoring, and vendor management as aspects of a single, continuous IRDAI compliance checklist helps to make audits more uniform and less intrusive. Early detection and resolution of problems using frequent VAPT and CERT in synchronized procedures lets you respond to the auditor’s noted deficiencies.
Working with a competent provider like Qualysec gives you clear reporting, technical know-how, and regulatory awareness all in one location. Combining your security strategy with national cyber requirements and IRDAI benefits your customers, your reputation, and your long-term business in addition to pleasing auditors.
Get a Free Sample Pentest Report

FAQs
Q1. Who needs IRDAI cybersecurity compliance in India?
All insurers, reinsurers, TPAs, brokers, business agents, web aggregators, insurance repositories, insurance information bureaus, and insure tech platforms handling policyholder data must follow the IRDAI information and cybersecurity standards and therefore the IRDAI cybersecurity criteria 2026Q2.
Q2. Is VAPT mandatory for IRDAI Certification?
Yes. The IRDAI cybersecurity audit needs application, network, and cloud VAPT as key inputs. As part of your continuous security plan, IRDAI expects you to regularly do VAPT for insurance firms, correct high-risk results, and maintain current reports.
Q3. How often must insurance companies perform cybersecurity audits?
Once every twelve months at least, and following significant system or architectural changes, usually, a complete cybersecurity audit, including VAPT, is required. To stay consistent with both IRDAI and CERT, some organizations opt for quarterly scans and more frequent internal audits. In ideas.
Q4. What is the penalty for non-compliance with IRDAI guidelines?
Penalties range from financial penalties to business operation restrictions, greater regulatory scrutiny, and, in extreme circumstances, suspension or revocation of certain permits. Aside from legal repercussions, violations and non-compliance might have severe reputational damage and consumer loss.
Q5. Does IRDAI Certification apply to insure tech startups?
Absolutely. Every digital platform that gathers, analyzes, or keeps policyholder information has to comply with the IRDAI data and cybersecurity requirements, regardless of company size or age. Startups can greatly gain from hiring a partner such as Qualysec early on so that adherence is embedded into their design instead of added on later.




































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0 Comments